Platinum Catalysts Chloroplatinic Acid 18497-13-7 H2PtCl6 with Competitive Price
-
Post Date:
Oct 12,2018
-
Expiry Date:
Oct 12,2019
-
Detailed Description:
Cas No. :18497-13-7
Quantity: 200tons/monthMetric Tons
Specs:Color:red 99%min
Price:200-300 USD Kilograms
Payment Method: TT LC Western Union Paypal
Chloroplatinic acid or hexachloroplatinic acid is the chemical compound usually found as the hexahydrate with the formula H2PtCl6·(H2O)6. This is one of the most readily available soluble compounds of platinum. It is rarely obtained in the pure state. The commercial product is the hydronium salt of the hexachloroplatinate(IV) anion. Therefore, the correct formula is [H3O]2[PtCl6]·4H2O.The related palladium compound, [H3O]2[PdCl6], is extremely unstable and has not been isolated in pure form.
Specification:
Identification
Name
Chloroplatinic acid
Synonyms
Chloroplatinic acid hexahydrate; Hexachloroplatinic acid hexahydrate
Molecular Formula
H2PtCl6.6(H2O)
Molecular Weight
517.90
CAS Registry Number
16941-12-1
EINECS
241-010-7
Platinum content
37.5%
Specification
Analytical pure
Nitrate
< 0.05%
Soluble substance in nitric acid
< 0.2%
Appearance
Orange yellow powder or red brown crystal
Application
Mainly used in preparing noble metal catalyst and noble metal coating, plating
Applications:
Potassium determination
See also: Potassium hexachloroplatinate
Chloroplatinic acid was popularized for the determination of potassium. The potassium is selectively precipitated as potassium chloroplatinate. Determinations were done in 85% (v/v) alcohol solutions with excess platinate ions, and the precipitated product was weighed. Potassium could be detected for solutions as dilute as 0.02 to 0.2% (m/v).
This method for determination of potassium was advantageous vs. the cobaltinitrite method used previously, since it required a single precipitation reaction.[citation needed] Today, the concentration of potassium is determined with an ion-selective electrode. These modern methods remain subject to interference.
Purification of platinum
See also: Ammonium hexachloroplatinate
Treatment with an ammonium salt, such as ammonium chloride, gives ammonium hexachloroplatinate,which is very insoluble in ammonium solutions. Heating the ammonium salt in hydrogen reduces it to elemental platinum. Platinum is often isolated from ores or recycled from residues thus.
Catalysis
Like many platinum compounds, chloroplatinic acid is used in catalysis. This compound was first reported by John Speier and colleagues from Dow Corning Corporation to catalyze the reaction of silyl hydrides with olefins, hydrosilylation. Typical of his reactions, Speier used isopropanol solutions containing trichlorosilane (SiHCl3), and methyldichlorosilane (CH3HSiCl2), with pentenes. Prior work on the addition of silanes to alkenes required radical reactions that were inefficient. It is generally agreed that chloroplatinic acid is a catalyst precursor. A possible role for colloidal platinum or zero-valentcomplexes has also been considered.
-
CAS Registry Number:
18497-13-7
-
Synonyms:
;Platinate(2-), hexachloro-, dihydrogen, hexahydrate;Dihydrogen hexachloroplatinate hexahydrate;Hydrogen hexachloroplatinate(IV) hexahydrate;Platinum chloric acid dihydrochloride hexahydrate;Dihydrogen hexachloroplatinate(IV) hexahydrate;Platinate(2-), hexachloro-, dihydrogen, hexahydrate, (OC-6-11)-;Hexachloroplatinic acid hydrate;Hydrogen hexachloroplatinate(IV) hydrate;hydrogen hexachloroplatinate(2-) hydrate (2:1:6);Hexachloroplatinic(IV) acid 6H2O;
-
Molecular Formula:
H4Cl6OPt
-
Molecular Weight:
427.8332
-
Molecular Structure:
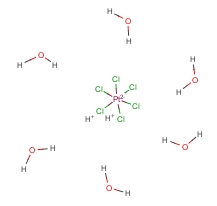
-
Hazard Symbols:
 T:Toxic;
T:Toxic;
-
Risk Codes:
R25:Toxic if swallowed.;
R41:Risks of serious damage to eyes.;
R42/43:May cause sensitization by inhalation and skin contact.;
-
Safety Description:
S22:Do not inhale dust.;
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.;
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.;
S45:In case of accident of if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label where possible).;
-
Company:
Zibo Jiashitai Chemical Technology Co.,Ltd
[ China ]
-
Contact:
Debby Xu
-
Tel:
8605333121112
-
Fax:
8605333129202
-
Email:
export03@jstchemical.com
Inquiry

T:Toxic;