Home > Offer to Sell > Catalyst and Auxiliary > Other Auxiliary Agent > Air Purification Activated Carbon
Air Purification Activated Carbon
Inquiry
| Post Date: | Sep 04,2018 |
| Expiry Date: | Sep 04,2019 |
| Detailed Description: |
Cas No. :7440-44-0;16291-96-6;90597-58-3;90452-98-5;83138-28-7;82600-5;64365-11-3;1333-85-3
Quantity: 100Metric Tons Specs:1.5, 2, 3, 4mm, 4-325mesh Price:1500 USD Metric Tons Payment Method: TT Air Purification Activated Carbon The structure of air purification activated carbon is relatively complicated, composed of planar layer of arranging in hexagonal carbon atoms, these planes are not arranged entirely along the common vertical axis, but layer and layer with an angular displacement, is messy and irregular, such a structure called the "whorl like structure". In the process of activation, all kinds of carbon compounds and disordered carbon between basic microcrystalline are cleared, created a space, the accumulations of remaining carbon are quite loose, but the mutual coupling is quite strong. Therefore between crystallite have many spaces with different shape, size and certain strength. According to the aperture size these spaces are generally divided into big pore, mid-hole and micropore. 90% specific surface area of activated carbon comes from micropore, its specific surface area can reach more than 1000m2/g, and pore volume also is large, so micropore is an important factor decided adsorption performance of air purification activated carbon The influencing factors of adsorption The adsorption characteristics of activated carbon not only depend on its pore structures, but also depend on its chemical compositions. 1) When activated carbon is activated, part of basic microcrystal has been burned, the disturbance of incomplete graphite layer changed the arrangement of the carbon skeleton electron cloud, appeared incomplete saturation valence and paired electrons, directly affect the adsorption properties of activated carbon. 2) Heteroatoms in the structure of activated carbon. There are two sources of heteroatoms: One kind is combined with chemical elements, such as oxygen and hydrogen. These elements are usually derived from raw materials, been left over due to in the carbonization can’t completely decomposed. Some combined with activating agent for chemical reaction bonded on the surface of the activated carbon while been activated. Another kind is ASH, it mainly comes from raw materials of activated carbon, little come from production process. Ash content of activated carbon lets microcrystal having structure defects, oxygen is chemical adsorbed on these defects, therefore improve the activated carbon adsorption capacity of polar molecules. The presence of ash on the gas adsorption (such as sulfur dioxide, water vapor, acetic acid) also has a direct effect. 3) Adding some inorganic compound (such as AlCl3, NaON, CuO) can let activated carbon modified, adsorption capacity changed greatly, and there are special effect to some substances. 4) C-O surface compounds, such as C-O surface complexes, surface oxide, surface oxidation compounds and chemical adsorption oxygen. These compounds were divided into two categories: One kind is when the temperature is below 100, gaseous oxygen combined with activated carbon surface for chemical reaction produced oxygen complexes, by hydration generated hydroxyl and other basic groups, and these basic groups can play the role of ion exchange. When heated to 1000 ℃, is generated gaseous oxide removed from activated carbon surface. Another kind is under 300~500℃, oxygen contact with activated carbon produced acidic oxide, by hydration generated acidic surface compounds, also have the ability of ion exchange. The functional groups produced by combination of surface oxygen are hydroxyl, carboxyl, phenolic, fat, quinone. But only a portion of oxygen in these functional groups, the rest is ether chain bound with carbon surface. 5) In the activated carbon, also combined with N, Cl and other elements, the combination of these atoms also has obvious effect on the adsorption properties of activated carbon. Activated carbon modified Research shows that the surface chemical properties of activated carbon are mainly determined by its surface chemical functional groups, surface heteroatoms and surface compounds. Among them, activated carbon surface groups are divided into oxygen-containing functional groups and nitrogen-containing functional groups. Oxygen-containing functional groups can be divided into acidic oxygen-containing functional groups and alkaline oxygen-containing functional groups, Acidic oxygen-containing functional groups including carboxyl, phenolic hydroxyl, lactone base, ring-type peroxy radical, quinone carbonyl. Alkaline oxygen-containing functional groups include similar pyrone structure groups etc. Acidic oxide makes active carbon having the nature of polarity, and is conducive to the adsorption of strong polar compounds. Alkaline compounds are easy to adsorb polar and nonpolar substances. It is generally believed that oxygen-containing functional groups and nitrogen-containing functional groups are mainly the result of raw materials incomplete carbonization, or is in the process of activated carbon combined with activated agent for chemical reaction bonded on the surface. The surface of common active carbon possesses nonpolar and hydrophobic, to indoor gas adsorption are mainly physical adsorption, can adsorb almost all of the gases. However, only physical adsorption is extremely small adsorption ability, practical value is very small. Furthermore, active carbon is a hydrophobic material, sometimes lack of adsorption capacity of hydrophilic substances, in addition the stability of physical adsorption is poor, and it is easy desorption and causes secondary pollution when temperature, pressure and other conditions change. Some Indoor pollutants are polarity, some are nonpolar: formaldehyde (polarity), benzene (nonpolar), toluene (weak polarity), p-xylene (nonpolar), o-xylene (polarity), meta-xylene (polarity), TVOC (total volatile organic compounds), ammonia (polarity), radon gas (nonpolar). Surface chemical modification is mainly to change the acid and alkali of activated carbon surface, adding and removing some surface functional groups, making it has some kind of special adsorption and catalytic properties. To the modification research of activated carbon, is mainly concentrated in the oxidative modification, deoxidization modification and modification by loading heteroatoms and compounds. Because indoor air mixtures have complex sources, some are polarity, and some are non-polarity, which need activated carbon to be modified so that it can adsorb most gaseous pollutants. 1) Oxidative modification Under appropriate conditions, the surface treatment of activated carbon by strong oxygenant can improve the content of acidic groups, which can enhance the adsorption capacity of polar materials, thus achieve the purpose of recycling or waste water treatment. Oxygenant includes: HNO3, H2SO4, HCl, HClO, HF, H2O2, O3, etc. 2) Deoxidization modification Under the appropriate temperature, the deoxidization modification of surface functional groups by deoxidizer on the surface of activated carbon can improve the relative content of alkaline groups, and enhance the non-polarity of activated carbon surface, thus improve the adsorption properties to nonpolar substances. The methods of deoxidization modification are mainly concentrated on high temperature treatment on activated carbon by H, N and other inert gases, as well as ammonia impregnation. 3) Modification via loading heteroatoms and compounds Via liquid phase deposition method adds the particular heteroatoms and compounds on the surface of activated carbon, using the combination of these substances and adsorbate to improve the adsorption performance of active carbon. Generally used includes Cu(NO3)2, Na2CO3, FeSO4, KMnO4, etc. The adsorption process of activated carbon The adsorption characteristics of activated carbon depend on its pore structures and the surface chemical properties, and surface chemical properties determine the chemical adsorption of active carbon. Activated carbon for gas adsorption includes physical adsorption and chemical adsorption, generally both been accompanied by simultaneous. Physical adsorption simply via attractive forces between molecules adsorbs adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. Physical adsorption is reversible, reducing adsorbent partial pressure in the gas phase, increasing the adsorption temperature, adsorbent quickly desorption, without changing its chemical composition. Chemical absorption has high selectivity, and a kind of adsorbent only has the effect to the specific substance. Chemical adsorption is irreversible, after adsorption adsorbent has changed the original characteristics. |
| CAS Registry Number: | 7440-44-0;16291-96-6;90597-58-3;90452-98-5;83138-28-7;82600-5;64365-11-3;1333-85-3 |
| Synonyms: | ;Whetlerite;Charcoal, except activated;HSDB 2017;Swine fly ash;Charcoal briquettes, shell, screenings, wood, etc.;NA1361;activated carbon;Graphite flake;activate carbon;coal based activated carbon;coal base activated carbon;Carbon;Activated carbon,coal;Medicinal Charcoal;active carbon;Charcoal actived; |
| Molecular Formula: | C |
| Molecular Weight: | 12.01 |
| Molecular Structure: | 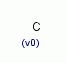
|
| Hazard Symbols: |  Xi:Irritant; Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Codes: | R36/37/38:; |
| Safety Description: | S24/25‖S22:; |
| Company: | Yuanying Industry Limited [ China ] |
| Contact: | Earuler Wang |
| Tel: | +86-15179996644 |
| Fax: | +86-799-6859700 |
| Email: | shiyu666@gmail.com |
-
Disclaimer statement:The information and data included above have been realized by the enterprises and compiled by the staff, and are subject to change without notice to you. The Chemnet makes no warranties or representations whatsoever regarding the facticity, accuracy and validity of such information and data. In order to ensure your interest, we suggest you chose the products posted by our gold suppliers or VIP members.